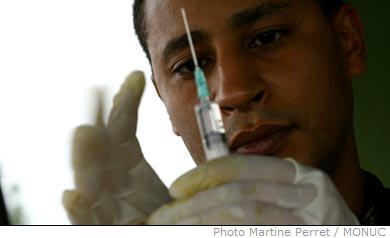
The Ministry of Health of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has on 16 February 2009 declared the end of the Ebola epidemic in the Mweka and Luebo health zones in the Province of Kasai Occidental . The last person to be infected by the virus died on 1 January 2009. This is more than double the maximum incubation period (42 days) for Ebola.
As of today, the health authorities have reported a total of 32 cases, including 15 deaths from Ebola. These 32 cases include confirmed, probable and suspect cases. During this outbreak, the Ebola virus was confirmed by laboratory tests at the Institut National de Recherches Biologiques (INRB) in Kinshasa, the Centre International de Recherches Médicales de Franceville (CIRMF) in Gabon, and the National Institute for Communicable Diseases (NICD), South Africa.
The WHO Country Office, Regional Office and Headquarters supported the MoH in Kinshasa and in the field at the location of the outbreak. The international response to the outbreak also involved UNICEF, the United Nations Organization Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUC), and the World Food Programme (WFP), as well as support from Caritas (Belgium), and the Congolese (DRC) Red Cross, together with partners in the Global Outbreak Alert and Response Network (GOARN), including the National Microbiology Laboratory (NML) of the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC), CIRMF, and NICD, and Médecins Sans Frontières (Belgium).
Related articles
- • UN Security Council Calls on Rwanda to Stop Supporting M23 Rebels in DR Congo (February 22, 2025)
- • 'Deadly environment' plus 'political and social' obstacles hinder Ebola fight, Security Council hears (July 24, 2019)
- • Ebola outbreak declared an international Public Health Emergency (July 17, 2019)
- • At least 30 dead after massacres in Ituri (March 2, 2018)
- • DR Congo: The country that knows how to beat Ebola (December 11, 2014)
- • ICC Confirms 14-Year Sentence Against Thomas Lubanga (December 1, 2014)
- • Ebola Epidemic Resurfaces in DR Congo's Equateur Province (August 25, 2014)
- • ICC sentences Germain Katanga to 12 years (May 23, 2014)
- • ICC finds Germain Katanga guilty of war crimes and crime against humanity (March 7, 2014)
- • Bosco Ntaganda Attacked Civilians on Ethnic Grounds, ICC Prosecutor Says (February 10, 2014)
- • Rebel Leader Bosco Ntaganda Makes First Appearence Before the ICC (March 26, 2013)
- • Bosco Ntaganda in the International Criminal Court's custody (March 22, 2013)
- • International Criminal Court Acquits Mathieu Ngudjolo Chui (December 18, 2012)
- • Thousands of Women March Against M23 Rebels in Kinshasa (November 24, 2012)
- • ICC Prosecutor Seeks 30 Years for Thomas Lubanga (June 13, 2012)
- • ICC Prosecutor Seeks New Charges Against Ntaganda, FDLR Leader (May 14, 2012)
- • Kabila's Position on The Arrest of Ntaganda 'Has Not Changed' (April 13, 2012)
- • DR Congo Government Warns Bosco Ntaganda He May Face Justice (April 6, 2012)
- • Thomas Lubanga found guilty of using child soldiers (March 14, 2012)
- • Tshisekedi Says He Won, Can He Prove It? (December 17, 2011)
- • Tshisekedi's Mental Health Called into Question after Incoherent Statements (November 8, 2011)
- • Security Council extends mandate of UN mission in DR Congo (June 28, 2011)
- • UN high-level HIV-AIDS meeting continues with progress reports (June 9, 2011)
- • Rights Groups: Strengthen Civilian Protection Before Elections (June 9, 2011)
- • Rape study 'questionable' (May 18, 2011)
- • Militiamen Sent to Testify in Warlords Trials at ICC (March 28, 2011)
- • UN Sanctions FDLR Leaders, CNDP Rebel Commander Integrated into Army (December 2, 2010)
- • UN launches patrols to head off rebel violence during holiday season (December 1, 2010)
- • 2010 Human Development Report analyses long-term development trends (November 4, 2010)
- • Congo Defense Minister Rejects UN Allegations against Army (October 17, 2010)
Tags: |







