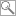Photo: Gratien Ira/IRIN  |
| Clashes between various armed groups in North Kivu have displaced tens of thousands of people |
MASISI, 25 October 2007 (IRIN) - At Masisi hospital in eastern Democratic Republic of Congo's North Kivu province, ill and wounded women shifted uncomfortably in their beds as several men and youths in uniform picked at bandages covering their gunshot wounds.
These patients received visits from local heads of some of the many armed groups active in eastern DRC.
It was therefore surprising to hear that none of the patients were injured in battle. According to their commanders, the injuries, including bullet wounds, were mostly accidental.
Officially, there are just two groups fighting in North Kivu: the DRC army - whose injured troops were present in droves in Masisi hospital - and forces loyal to dissident General Laurent Nkunda.
But the army stands accused of co-opting other armed groups, both domestic and from neighbouring states, to purge Nkunda's fighting force from the region.
The government in Kinshasa, and some of the groups themselves, deny any formal alliance has taken place.
"We have not been asked to support the Congolese army and we are not doing so," said Bravo Jean-Bernard, the local head of the Forces Démocratiques de la Libération du Rwanda (FDLR). "We are not fighting against Nkunda's troops."
Asked why members of the FDLR were in the hospital with gunshot wounds, Jean-Bernard said: "We came here for different diseases. But none of them have to do with war."
Rwandan link
Leaders of armed groups in eastern DRC often evade pointed questions about their tactics. They claim to be fighting on idealistic or patriotic grounds and deny accusations by human rights groups of involvement in crimes such as murder, rape and recruitment of children.
The FDLR comprises of Rwandan Hutus who fought against Rwandan troops and allied DRC rebels during the civil war that raged in the east of the DRC between 1998 and 2003. Many in the FDLR used to be members of the Interahamwe, the militia that carried out much of the killing during Rwanda's 1994 genocide.
Rwandan President Paul Kagame twice justified his invasion of DRC, in 1996 and 1998, by evoking the threat posed by the FDLR and other "negative forces".
In 2005, the FDLR announced it was ending its armed struggle against Rwanda's Tutsi-led government, but it has yet to hand over its weapons.
"We are here because Kagame will not allow us to return home," said Jean-Bernard. "We want to change his government, but we will not act militarily, we will act politically."
Asked to detail the FDLR's political programme, Jean Bernard told IRIN: "That is a strategic secret."
Mayi Mayi
Also at the hospital in Masisi to visit troops who had sustained "accidental" wounds, was Daniel Baloume, the second-in-command of the Patriotes Résistants du Congo (Coalition of Patriots in the Congolese Resistance PARECO).
PARECO is the emerging political wing of the wide range of community-based militias collectively known as Mayi Mayi. These self-styled civil defence units rose to prominence during the 1998-2003 war, with the aim of protecting villages from invading Rwandan troops.
Since the end of the war, the Mayi Mayi have been accused of crimes such as banditry, rape and murder.
Aware of their reputation, the political wing has opted for a change. "Everyone calls us the Mayi, Mayi," said Baloume, "so we decided to have our own special name."
Beyond the name, PARECO's political plans, like the FDLR's, are hard to pin down beyond a stated desire to quell Nkunda's uprising and bring peace to eastern DRC.
"Anyone who does not want peace is our enemy," Baloume told IRIN. "Nkunda is our enemy because he will not join the Congolese army."
But PARECO denies taking part in the current fighting.
Brassage
The DRC government says pacifying the east depends on integrating all armed groups into the regular army, a process known locally as 'brassage'.
"We accept to go to 'brassage'," Baloume told IRIN. "But not until Nkunda goes first."
Rebel general Nkunda, an ethnic Tutsi and former member of the Rassemblement Congolais pour la Démocratie, a now-defunct rebel group backed by Rwanda, cut short his own 'brassage' in 2004, saying the government had not done enough to rid the eastern provinces of the FDLR.
Many analysts and observers on the ground believe Nkunda is supported by Rwanda's Tutsi-dominated administration, an accusation denied by Kigali, even if President Kagame concedes that Nkunda has legitimate grievances.
While the conflict in Congo is often portrayed by the leaders of armed groups as a struggle for the rights of ethnic communities, analysts say it is these very civilians who have borne the brunt of the ongoing conflict.
Humanitarian impact
"Every time there is fighting between the Congolese government, Nkunda and the Hutu militias in eastern Congo, the primary victims are the civilian population," says Jason Stearns, an independent political analyst in the region.
Incidents of murder, rape, looting, recruitment of children into armed groups and forced displacement of civilians have skyrocketed since fighting erupted between Nkunda's forces and the regular army in December 2006.
The UN estimates 370,000 people have fled their homes since late 2006, many of them settling in squalid camps for the displaced where they face hunger and disease.
Humanitarian groups have been struggling to reach tens of thousands of civilians cut off by fighting.
FDLR's Jean-Bernard declined to comment directly on the humanitarian consequences of the ongoing violence in eastern Congo.
"We did not start this fight," he said.
nk/eo/am/sr